Key Difference Between Standard And Next Generation Firewalls
- Key Difference Between Standard And Next Generation Firewalls Wiki
- Key Difference Between Standard And Next Generation Firewalls For Dummies Pdf
- A Key Difference Between Standard And Next Generation Firewalls Is Which Of The Following
- Key Difference Between Standard And Next Generation Firewalls Provide All Of The Following Except
Although some people use the terms interchangeably, there are key differences. As we explain below, next-generation firewalls are typically defined as firewalls enhanced with intrusion prevention and application intelligence. On the other hand, UTM systems include those features—plus. What is a next-generation firewall? A next-generation firewall (NGFW) is a network security device that provides capabilities beyond a traditional, stateful firewall. Support: Your next-generation firewall setup page These resources will assist you in setting up your next-generation firewall, starting with onboarding. Solution overview.
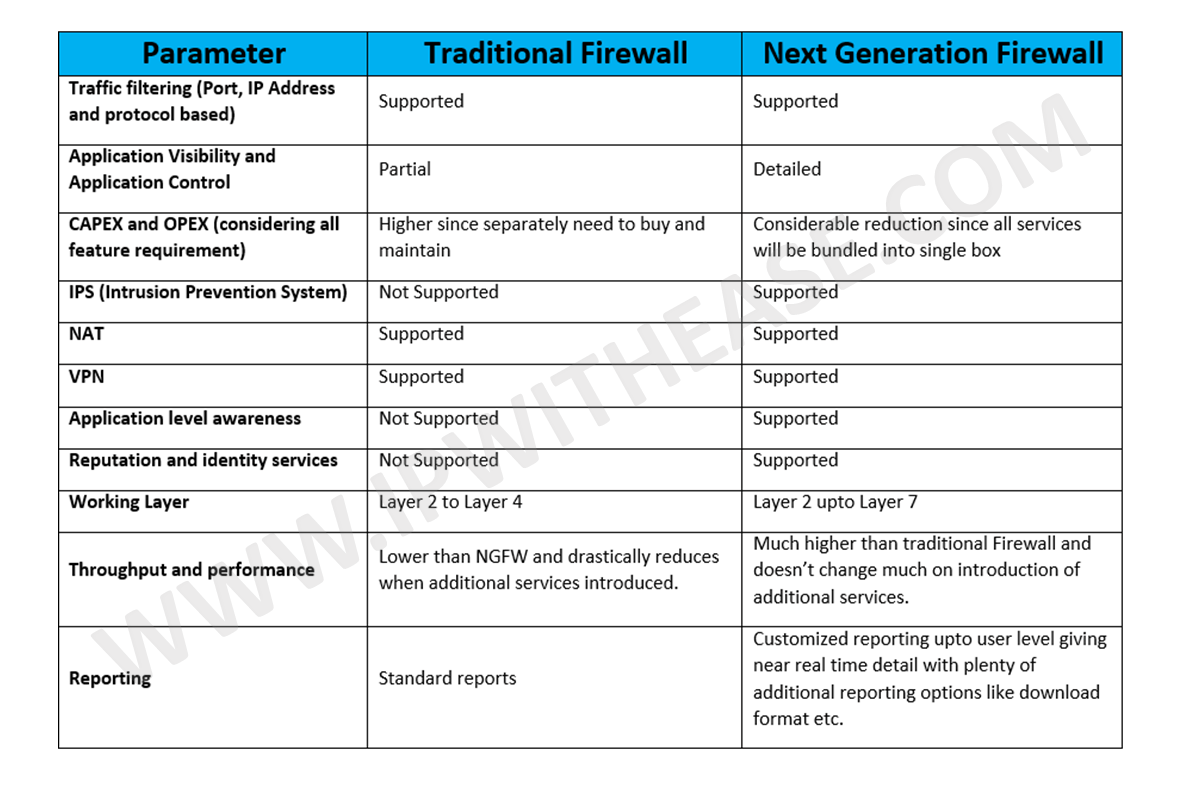
A next-generation firewall (NGFW) is a part of the third generation of firewall technology, combining a traditional firewall with other network device filtering functions, such as an application firewall using in-line deep packet inspection (DPI), an intrusion prevention system (IPS). Other techniques might also be employed, such as TLS/SSL encrypted traffic inspection, website filtering, QoS/bandwidth management, antivirus inspection and third-party identity management integration (i.e. LDAP, RADIUS, Active Directory).[1]
- Next Generation Firewall vs Web Application Firewall. Date posted: 9th June 2015. Next Generation Firewalls enable policy based visibility and control over applications, users and content using three unique identification technologies: App-ID, User-ID and Content-ID.
- Firewalls for your Business - Info, Pricing, & Comparisons - Find the firewall perfectly fit for your network, no matter the size. Our team of highly-certified experts can help with any network, any deployment, and any environment!
- Oct 07, 2011 A: A Next Generation Firewall (aka Application Firewall) is a security device, evolution of a stateful firewall, that is application aware, i.e. Capable to recognize and block applications according to specific patterns and fingerprints peculiar of the application itself. Its security paradigm is to prevent users from bypassing the layer of.
Next-generation firewall vs. traditional firewall[edit]
NGFWs include the typical functions of traditional firewalls such as packet filtering,[2] network- and port-address translation (NAT), stateful inspection, and virtual private network (VPN) support. The goal of next-generation firewalls is to include more layers of the OSI model, improving filtering of network traffic that is dependent on the packet contents.
NGFWs perform deeper inspection compared to stateful inspection performed by the first- and second-generation firewalls.[3] NGFWs use a more thorough inspection style, checking packet payloads and matching signatures for harmful activities such as exploitable attacks and malware.[4]
Evolution of next-generation firewalls[edit]
Improved detection of encrypted applications and intrusion prevention service. Modern threats like web-based malware attacks, targeted attacks, application-layer attacks, and more have had a significantly negative effect on the threat landscape. In fact, more than 80% of all new malware and intrusion attempts are exploiting weaknesses in applications, as opposed to weaknesses in networking components and services.
Stateful firewalls with simple packet filtering capabilities were efficient blocking unwanted applications as most applications met the port-protocol expectations. Administrators could promptly prevent an unsafe application from being accessed by users by blocking the associated ports and protocols. But blocking a web application that uses port 80 by closing the port would also mean complications with the entire HTTP protocol.
Protection based on ports, protocols, IP addresses is no more reliable and viable. This has led to the development of identity-based security approach, which takes organizations a step ahead of conventional security appliances which bind security to IP-addresses.
NGFWs offer administrators a deeper awareness of and control over individual applications, along with deeper inspection capabilities by the firewall. Administrators can create very granular 'allow/deny' rules for controlling use of websites and applications in the network.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^Intro to Next Generation Firewalls - By Eric Geier, 06 September, 2011
- ^Next gen security - by Ben Rossi - 07 August, 2012
- ^Next-generation firewalls: Security without compromising performance - By Patrick Sweeney, 17 October 2012
- ^Next-Generation Firewalls 101 - By Frank J. Ohlhorst, 1 March 2013
Key Difference Between Standard And Next Generation Firewalls Wiki
A next-generation firewall (NGFW) is a part of the third generation of firewall technology, combining a traditional firewall with other network device filtering functions, such as an application firewall using in-line deep packet inspection (DPI), an intrusion prevention system (IPS). Other techniques might also be employed, such as TLS/SSL encrypted traffic inspection, website filtering, QoS/bandwidth management, antivirus inspection and third-party identity management integration (i.e. LDAP, RADIUS, Active Directory).[1]
Next-generation firewall vs. traditional firewall[edit]
NGFWs include the typical functions of traditional firewalls such as packet filtering,[2] network- and port-address translation (NAT), stateful inspection, and virtual private network (VPN) support. The goal of next-generation firewalls is to include more layers of the OSI model, improving filtering of network traffic that is dependent on the packet contents.
NGFWs perform deeper inspection compared to stateful inspection performed by the first- and second-generation firewalls.[3] NGFWs use a more thorough inspection style, checking packet payloads and matching signatures for harmful activities such as exploitable attacks and malware.[4]
Evolution of next-generation firewalls[edit]
Improved detection of encrypted applications and intrusion prevention service. Modern threats like web-based malware attacks, targeted attacks, application-layer attacks, and more have had a significantly negative effect on the threat landscape. In fact, more than 80% of all new malware and intrusion attempts are exploiting weaknesses in applications, as opposed to weaknesses in networking components and services.
Stateful firewalls with simple packet filtering capabilities were efficient blocking unwanted applications as most applications met the port-protocol expectations. Administrators could promptly prevent an unsafe application from being accessed by users by blocking the associated ports and protocols. But blocking a web application that uses port 80 by closing the port would also mean complications with the entire HTTP protocol.
Protection based on ports, protocols, IP addresses is no more reliable and viable. This has led to the development of identity-based security approach, which takes organizations a step ahead of conventional security appliances which bind security to IP-addresses.
NGFWs offer administrators a deeper awareness of and control over individual applications, along with deeper inspection capabilities by the firewall. Administrators can create very granular 'allow/deny' rules for controlling use of websites and applications in the network.
See also[edit]
Key Difference Between Standard And Next Generation Firewalls For Dummies Pdf
References[edit]
A Key Difference Between Standard And Next Generation Firewalls Is Which Of The Following
- ^Intro to Next Generation Firewalls - By Eric Geier, 06 September, 2011
- ^Next gen security - by Ben Rossi - 07 August, 2012
- ^Next-generation firewalls: Security without compromising performance - By Patrick Sweeney, 17 October 2012
- ^Next-Generation Firewalls 101 - By Frank J. Ohlhorst, 1 March 2013
